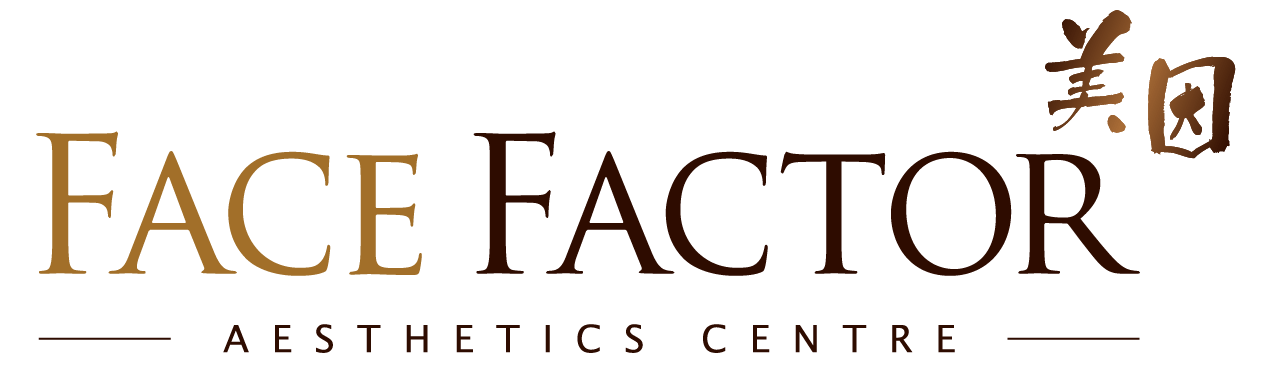PicoLo fourth-generation ultra-picosecond laser
Origin: South Korea
PICOS picosecond laser is a brand-new laser technology, using the shortest pulse at present, it can release more energy in a short time and effectively shatter stubborn melanin. Since the energy stays on the skin for a shorter and more precise time, it does not harm the surrounding skin tissue of the treatment area, preventing the phenomenon of anti-darkness (melanin hyperplasia) after the treatment.
Instrument Features
Uniform energy output to improve treatment safety
Reduce anti-black function, improve treatment comfort and shorten recovery period
The treatment is more flexible, more effective, and the number of treatments is shortened
especially suitable for
Remove pigment
skin rejuvenation
Improve uneven skin tone and pigmentation
Improve enlarged pores
Smoothes acne scars and fine lines
Pigments after nano-second laser irradiation
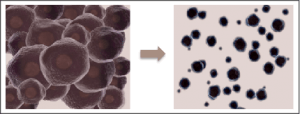
Pigments after pico-second laser irradiation
- Dual Wavelength Laser: The two wavelengths (1064nm/532nm) can penetrate into layers of skin and tackle both epidermal and dermal pigments.
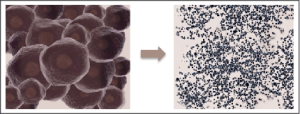
- High Peak Energy: Thermal Relaxation Time(TRT) of pigment is lower than 10 nanoseconds. Comparing with the nanosecond mode, the pulse duration of PICOS(150ps) is 100 times shorter than general Q-switched Nd:YAGlaser(10ns). With the same energy density, PICOS makes a more effective treatment due to its high peak energy and minimum level of surrounding skin damage.
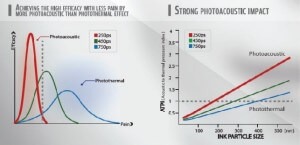
Photoacoustic Mechanism: Unlike traditional laser, PICOS uses photoacoustic mechanism to eliminate pigments. The use of focusing lens allows energy to concentrate on a tiny spot, which effectively breaks down the concentrated melanin without damaging surrounding skin tissues. It also minimizes discomfort during treatment, limits melasma recurrence, and speed up recovery.
Efficacy:
- Epidermal Pigments: Solar lentigo, Freckles, Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation, Seborrheic Keratosis, Café au lait spots, etc.
- Dermal Pigments: Nevus of Ota, Nevus of Ito, Blue nevus, Becker’s nevus, Melasma, Acquired Dermal Melanocytosis, etc.